What are memories?
In short, memories are the collective data of our past in order to or influence our current behavior.
History of memory
Before we go deeper, we have to look at our past, how memory comes into the picture of neuroscience. In 1953, there was a person whose name was Henry Molasium who met an accident while riding a bicycle. In this accident, he got damage to his skull and spending a few days in hospital he came back home.Due to his damaged skull which couldn't be repair by doctors, he began to experience severe seizures. Then doctors decided to remove the part of the brain which was responsible for seizures.
Parts that should be removed from the left and right temporal lobes are mainly the Hippocampus, Amygdala, and part of the entorhinal cortex.
Seizures were completely stop, but he began to suffer from anterograde amnesia. It means he will lose his ability to form new memories.
Doctors were trying to figure this out but until 1950 there was no idea about memories and thus research started on memories.
Henry Molasium (H.M) starts forgetting things which include facts and ideas but he can learn habits like riding a bicycle or learning new dance steps.
Memories are of different types because H.M can able to remember certain memories. So memories are classified into different groups and they are:-
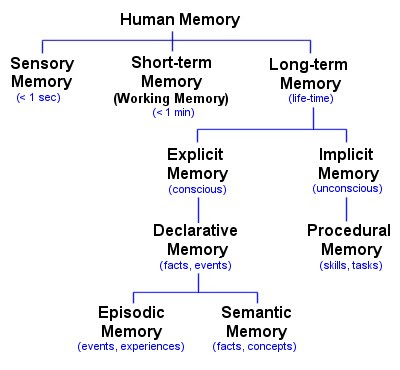
- The Amygdala used to store the emotional responses.
- Motor memory is store in Cerebellum
- Memories of facts and events are store in Thalamus and Hypothalamus which is located in the medial temporal lobe.
How does memory is form?
Memory is nothing but firing of neurons when we experience something. our brain talks with the help of neurons and neurons communicate with the help of synaptic connections.After doing something repeatedly, neurons connected to that task will get stronger and eventually make a neural circuitry.
Neural circuitry will become more efficient in communicating the message and this will make a shift to Long Term Memory.
while neurons that do not get involve much, will get weaker and serve no purpose to be alive. Neurons that fire together, wire together.
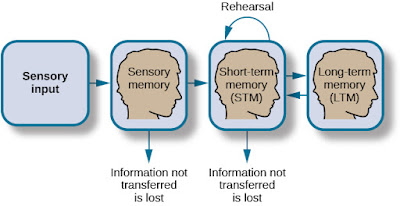
After sensory memory it will store in the gray matter i.e. in cortex in the form of short term memory. This memory will last up to 60 sec, short term memory is also known as working memory for e.g short-term memory can be used to remember a phone number. After experiencing STM for a long time it will go through the hippocampus where a group of proteins will work together and will make that memory to long term memory in the cortex. Where it will be store as a permanently for a lifetime.
Why do we lose memories?
When we experience something like riding a bicycle, that experience is converted into electrical energy that zips along with network of neurons. First information is available in short term memory and then will reside in the hippocampus after than will eventually become long term memory. Neurons in all our brains communicate with each other with the help of synapse using neurotransmitters.If two neurons continue to process information for a long time, they will become more efficient and this process is called Long Term Potentiation and will be there for the long term.


Depression and isolation can also be the cause,40% of depressed people are more likely to develop memory problems.
Feel Free to contact us with any questions.


0 Comments