What are neurons?
Neurons are cells within the nervous system that transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells. They communicate with each other with the help of neurotransmitters which get receive by another neuron through synaptic connection.
Our brain communicates with electrical pulses released by the nerve cells. Neurons are located in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system.
 |
| Image source:- Khan academy |
Central nervous system
It consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It is in the CNS that all of the analysis of information takes place.
Peripheral nervous system
It consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons.
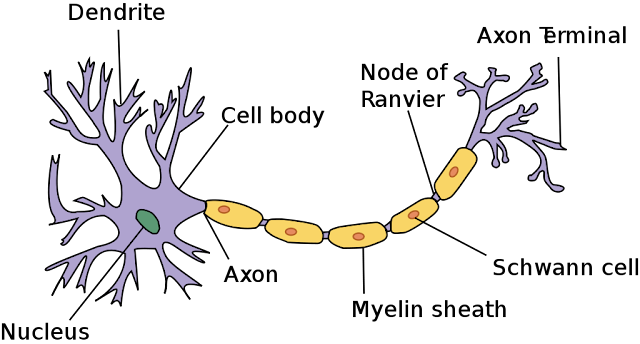
Anatomy of neurons
Neurons have mainly three parts, Axon, dendrites, and cell body(Soma).
Cell body or Soma
This main part has all of the necessary components of the cell, such as the nucleus (which contains DNA), endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes (for building proteins), and mitochondria (for making energy). If the cell body dies, the neuron dies.
Axon
This long, cablelike projection of the cell carries the electrochemical message (nerve impulse or action potential) along the length of the cell. Depending upon the type of neuron, axons can be cover with a thin layer of the myelin sheath, like an insulated electrical wire. Myelin is made of fat and protein, and it helps to speed transmission of a nerve impulse down a long axon. Myelinated neurons are typically found in the peripheral nerves (sensory and motor neurons), while non-myelinated neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord.
Dendrites
Incoming signals come from dendrites which are a branch-like projection on the cell body. Incoming signals can be either excitatory or inhibitory signals. At a time neurons may receive thousands of signals and according to that signals he will decide whether to fire a signal or not. The further signal passes through Axon.
Classifications of neurons
According to their functions, neurons can be classified into three types and they are Motor neurons, Sensory neurons, and interneurons.
Motor neurons
Motor neurons convey messages received by other neurons directly to muscles, glands, and organs. For example, if you pick up a hot cup of coffee then motor neurons will activate muscles of the hand and you will keep that cup on the table.
Sensory neurons
Sensory neurons will convey messages to CNS to be further processed. It gathers information from outside and inside of the body and conveys to CNS. For example, if you pick up a cup of hot coffee then sensory neurons will gather information and send it to CNS that it was really hot.
Interneurons
This type of neurons gather information from sensory neurons and send them to motor neurons. Interneurons can only be found in the Central nervous system. For example, if you picked up a hot cup of coffee, the signal from the sensory neurons in your fingertips would travel to interneurons in your spinal cord. Some of these interneurons would signal to the motor neurons controlling your hand muscles (causing you to let go), while others would transmit the signal up the spinal cord to neurons in the brain, where it would be perceived as pain.
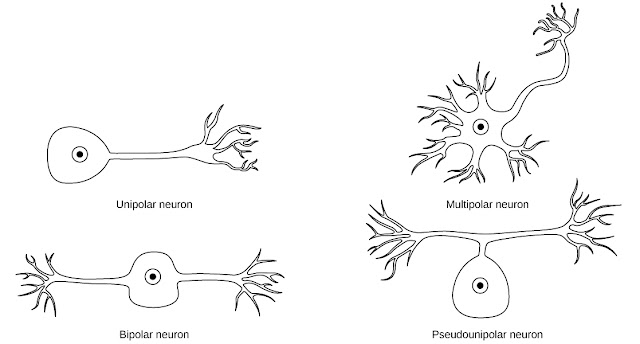
Neurons can also be classified on the basis of their structure, they are uni-polar, bi-polar, Multi-polar, and pseudo-unipolar.
What are neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messages that are being transmit by nerve cells to muscles. Communication between two neurons happens due to synaptic connections. Here, electrical signals that have travel along the axon are briefly convert into chemical ones through the release of neurotransmitters, causing a specific response in the receiving neuron.
A neurotransmitter influences a neuron in one of three ways: excitatory, inhibitory or modulatory.
Excitatory neurotransmitters
These types of neurotransmitters excite neurons to fire an action potential in other words which get their target cells all fired up with chemical energy. Some of the major excitatory neurotransmitters include epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
These types of neurotransmitters will make neuron to do not fire an action potential. Some of the major inhibitory neurotransmitters include serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
Some neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and dopamine, can create both excitatory and inhibitory effects depending upon the type of receptors that are present.
Modulatory neurotransmitters
These neurotransmitters often referred to as neuromodulators, are capable of affecting a larger number of neurons at the same time. These neuromodulators also influence the effects of other chemical messengers. Where synaptic neurotransmitters are released by axon terminals to have a fast-acting impact on other receptor neurons, neuromodulators diffuse across a larger area and are more slow-acting.
Neurotransmitters can also be classified broadly into monoamines, amino acids, and peptides.
Amino acids
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the body's main inhibitory chemical messenger. GABA contributes to the vision, motor control, and plays a role in the regulation of anxiety. Benzodiazepines, which are use to help treat anxiety, function by increasing the efficiency of GABA neurotransmitters, which can increase feelings of relaxation and calm.
- Glutamate is the most plentiful neurotransmitter found in the nervous system where it plays a role in cognitive functions such as memory and learning. Excessive amounts of glutamate can cause excitotoxicity resulting in cellular death. This excitotoxicity caused by glutamate build-up is associated with some diseases and brain injuries including Alzheimer's disease4, stroke, and epileptic seizures.
Peptides
- Oxytocin is both a hormone and a neurotransmitter. It is produce by the hypothalamus and plays a role in social recognition, bonding, and sexual reproduction. Synthetic oxytocin such as Pitocin is often use as an aid in labor and delivery. Both oxytocin and Pitocin cause the uterus to contract during labor.
- Endorphins are neurotransmitters than inhibits the transmission of pain signals and promote feelings of euphoria. These chemical messengers are produce naturally by the body in response to pain, but they can also be trigger by other activities such as aerobic exercise. For example, experiencing a "runner's high" is an example of pleasurable feelings generate by the production of endorphins.
Monoamines
- Epinephrine is consider as both a hormone and a neurotransmitter. Generally, epinephrine (adrenaline) is a stress hormone that is released by the adrenal system. However, it functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain.
- Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in alertness is involve in the body's fight or flight response. Its role is to help mobilize the body and brain to take action in times of danger or stress. Levels of this neurotransmitter are typically lowest during sleep and highest during times of stress.
- Histamine acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain and spinal cord. It plays a role in allergic reactions and is produced as part of the immune system's response to pathogens.
- Dopamine plays an important role in the coordination of body movements. Dopamine is also involved in reward, motivation, and addictions. Nine Several types of addictive drugs increase dopamine levels in the brain. Parkinson's disease, which is a degenerative disease that results in tremors and motor movement impairments, is caused by the loss of dopamine-generating neurons in the brain.
- Serotonin plays an important role in regulating and modulating mood, sleep, anxiety, sexuality, and appetite. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors usually referred to as SSRIs, are a type of antidepressant medication commonly prescribed to treat depression, anxiety, panic disorder, and panic attacks. SSRIs work to balance serotonin levels by blocking the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, which can help improve mood and reduce feelings of anxiety.


0 Comments